When were smartphones invented? This journey explores the fascinating evolution of mobile technology, from humble beginnings to the ubiquitous devices we use today. We’ll delve into the key moments, technological advancements, and societal impacts that shaped the smartphone’s rise to prominence.
This exploration delves into the defining characteristics of smartphones, comparing them to earlier mobile phones. It traces the development of prototypes and early devices, showcasing a timeline of key milestones. The discussion will highlight the birth of the modern smartphone, analyzing the factors that led to its widespread adoption, and exploring the impact on communication and society.
Defining Smartphones
Smartphones represent a significant evolution in mobile technology, transcending the capabilities of their predecessors, the feature phones. This shift wasn’t simply an incremental upgrade; it was a fundamental change in how we interact with technology and the world around us. They seamlessly integrated computing power with communication, transforming the mobile phone from a basic tool into a powerful personal computer.
What Constitutes a Smartphone?
A smartphone is a mobile phone with advanced computing capabilities beyond basic communication functions. Crucially, it runs a full-fledged operating system, like iOS or Android, enabling a broad range of applications. This distinguishes it from feature phones, which primarily offered voice calls and text messaging. This distinction hinges on the smartphone’s capacity for software execution, which enables the execution of a wide range of applications.
Key Features of a Smartphone
The defining features of a smartphone extend far beyond simply making calls and sending texts. These devices incorporate several key characteristics that set them apart.
- Touchscreen Interface: The majority of smartphones utilize touchscreens for input, allowing users to interact with applications and menus through intuitive gestures. This contrasts sharply with the physical keypad interfaces found in earlier mobile phones.
- Internet Connectivity: Smartphones are equipped with robust internet connectivity, enabling access to the vast world of online information, services, and applications. This seamless integration with the internet differentiates them from older models, which often lacked such capabilities.
- App Ecosystem: Smartphones support a vast ecosystem of applications, often referred to as apps. These applications enhance the device’s functionality, offering everything from productivity tools to entertainment options. The wide array of apps available distinguishes smartphones from their predecessors.
- Sophisticated Processing: The processing power of smartphones is significantly higher than that of feature phones. This increased processing capacity allows for the execution of complex tasks and the seamless operation of numerous applications simultaneously.
Technological Advancements Leading to Smartphones
The development of smartphones was not a sudden event but rather a culmination of several technological advancements. Key innovations include the miniaturization of components, the development of advanced processors, the improvement of battery technology, and the rise of high-speed mobile networks. These advances enabled the integration of complex computing capabilities into a handheld device.
- Miniaturization of Components: The ability to cram increasingly powerful components into smaller packages was crucial. This allowed for the integration of complex processors, memory, and other essential elements into a handheld device.
- Advancements in Processors: The development of more powerful and energy-efficient processors played a pivotal role. These advancements enabled the execution of complex tasks and the smooth operation of various applications on the device.
- Improved Battery Technology: Increased battery capacity and efficiency were essential for enabling prolonged use without frequent recharging. This was critical for transforming the mobile phone from a device used primarily for communication to a fully functional computing device.
- High-Speed Mobile Networks: The evolution of high-speed mobile networks, like 3G and 4G, enabled faster data transfer rates, crucial for the seamless operation of online applications and services.
Comparison of Smartphones and Feature Phones
The table below highlights the key differences between smartphones and feature phones.
| Feature | Feature Phone | Smartphone |
|---|---|---|
| Operating System | Basic operating system (if any) | Full-fledged operating system (iOS, Android, etc.) |
| Applications | Limited applications (e.g., basic games, calculators) | Vast ecosystem of applications |
| Internet Access | Limited or no internet access | Robust internet connectivity |
| Processing Power | Low processing power | High processing power |
| User Interface | Physical keypad or limited touchscreen | Touchscreen interface |
Early Pioneers and Prototypes
The journey towards the smartphones we know today wasn’t a sudden leap, but rather a gradual evolution fueled by innovation and technological advancements. Early mobile devices, while rudimentary by modern standards, laid the groundwork for the sophisticated smartphones we use daily. These initial explorations in mobile computing explored the potential and limitations of this emerging technology.The quest for mobile computing involved a diverse array of individuals and companies, each contributing unique insights and technologies.
From simple prototypes to more sophisticated experiments, these early efforts represent significant steps toward the ubiquitous nature of smartphones today. Understanding these early pioneers and their contributions offers valuable context for appreciating the complex development of mobile technology.
Key Individuals and Companies
Early mobile device development involved collaboration across various sectors, with numerous individuals and companies contributing crucial components. Radio engineers, computer scientists, and telecommunications experts played essential roles in advancing the field. Notable figures and companies include researchers at Bell Labs, who pioneered early cellular technologies, and Motorola, known for their significant contributions to portable communication devices.
Prototypes and Experimental Devices
Numerous prototypes and experimental devices emerged as the field evolved. Early mobile phones were often bulky and featured limited functionality compared to their modern counterparts. For example, the Motorola DynaTAC 8000x, introduced in 1983, was one of the first commercially available handheld mobile phones. This device, while revolutionary at the time, was large and had a short battery life, highlighting the constraints of early mobile technology.
Technological Limitations of Early Mobile Devices
Early mobile devices faced several technological limitations. Battery life was a major concern, as devices often required lengthy charging times and had short operational periods. Display technology was also rudimentary, restricting the user interface and overall usability. Limited memory capacity and processing power further constrained the functionalities of these early devices. These limitations influenced the development path, driving continuous innovation in areas like battery chemistry, display technology, and processor design.
Timeline of Mobile Technology Evolution
A timeline illustrating key milestones in the evolution of mobile technology reveals the progressive advancements that shaped smartphones.
| Year | Event | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1973 | Martin Cooper makes the first public mobile phone call | A significant landmark in mobile communication history, demonstrating the potential of handheld devices. |
| 1983 | Motorola DynaTAC 8000x released | First commercially available handheld mobile phone, marking a crucial step towards widespread adoption. |
| 1992 | First GSM mobile phone released | GSM technology became a significant factor in global mobile phone proliferation. |
| 1996 | IBM Simon Personal Communicator | Considered a pioneering smartphone prototype, featuring touch screen and other advanced functionalities. |
| 2000s | Advancements in mobile operating systems | The development of operating systems like Symbian and Palm OS laid the foundation for the user experience in modern smartphones. |
The Birth of the Modern Smartphone
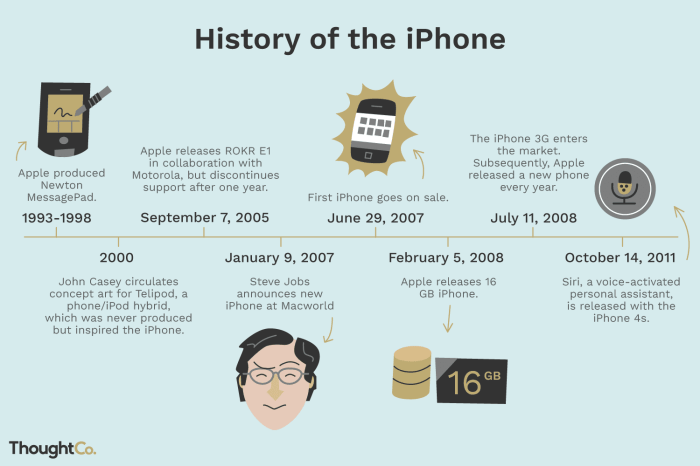
The evolution from early mobile phones to the ubiquitous smartphones we use today was a gradual process, driven by a confluence of technological advancements and market demands. This period witnessed the convergence of computing power, mobile connectivity, and user-friendly interfaces, leading to the devices we now consider essential. The shift wasn’t sudden, but rather a series of incremental improvements that culminated in the modern smartphone.The modern smartphone, characterized by its advanced computing capabilities, internet connectivity, and diverse applications, emerged from a foundation of previous mobile technologies.
Key factors like miniaturization of components, improved battery life, and the development of intuitive user interfaces played pivotal roles in the widespread adoption of smartphones. This period saw a remarkable increase in the processing power available within a compact device, fundamentally altering how we communicate and interact with information.
Key Events and Moments
The emergence of the modern smartphone wasn’t a singular event but rather a series of milestones. The introduction of touchscreens, advancements in mobile operating systems, and the increasing availability of high-speed internet access all contributed to the development of the modern smartphone. Key moments included the release of pioneering devices like the iPhone and the Android platform, which significantly influenced the smartphone market.
Influential Factors
Several factors converged to drive the widespread adoption of smartphones. Technological advancements, such as improved processors, larger displays, and enhanced connectivity, played a significant role. The increasing demand for mobile internet access and the desire for portable computing also fueled the evolution. The rise of app stores further contributed to the adoption, as they provided a platform for developers to create and distribute applications tailored to specific needs and interests.
Impact of First Commercially Successful Smartphones
The initial commercially successful smartphones, particularly the iPhone and early Android devices, revolutionized the mobile market. Their user-friendly interfaces, combined with access to a vast array of applications, redefined the functionality and potential of mobile devices. These devices effectively transitioned mobile phones from basic communication tools to powerful computing platforms, changing how people interacted with information, entertained themselves, and conducted business.
Operating Systems
The proliferation of smartphones led to the development of diverse operating systems. Each system offered unique features and functionalities, catering to different user needs and preferences.
| Operating System | Key Features | Early Devices |
|---|---|---|
| iOS | Intuitive user interface, focus on simplicity and aesthetics | iPhone |
| Android | Open-source platform, allowing for diverse customization and app development | Nexus One, HTC Dream |
| Windows Phone | Integration with Microsoft ecosystem, focus on business applications | Windows Phone 7 devices |
Key Technological Advancements
The evolution of smartphones wasn’t a single leap; it was a confluence of interconnected technological advancements. These innovations, from improved displays to faster processors, progressively enhanced the capabilities and usability of mobile devices, ultimately transforming them into the powerful computing tools we know today.
Touchscreen Development
The transition from physical buttons to touchscreens revolutionized user interaction. Early touchscreen prototypes, often utilizing resistive or capacitive technologies, presented challenges in accuracy and responsiveness. The development of advanced capacitive touchscreens, sensitive to multiple touches and pressure variations, marked a significant turning point. This evolution paved the way for intuitive interfaces, enabling users to navigate menus, input text, and interact with applications seamlessly.
Early implementations often featured limited resolution and slower processing, leading to sluggish performance. However, advancements in display technology, including increased pixel density and improved refresh rates, greatly improved the user experience. This allowed for more complex and visually appealing interfaces, further enhancing the appeal of smartphones. For example, the iPhone’s adoption of multi-touch technology, capable of handling multiple simultaneous inputs, set a new standard for mobile interaction.
Mobile Internet Connectivity
The rise of smartphones was intrinsically linked to the development of mobile internet connectivity. Early generations of mobile networks, like 2G, offered limited data transfer speeds, hindering the seamless streaming and downloading capabilities crucial for a modern smartphone experience. The introduction of 3G and later 4G technologies provided significantly faster data rates, enabling mobile browsing, video streaming, and app downloads.
The subsequent evolution to 5G further boosted data speeds and bandwidth, laying the foundation for today’s high-demand applications and services, such as cloud gaming and high-definition video conferencing.
Miniaturization and Battery Technology
Miniaturization played a crucial role in reducing the size and weight of smartphones while simultaneously increasing their processing power. The ability to pack powerful processors and memory chips into increasingly compact spaces was a key driver in smartphone evolution. As processing power increased, power consumption also rose, necessitating the advancement of battery technology. Improvements in battery capacity, density, and efficiency enabled longer operating times between charges.
For example, the development of lithium-ion batteries provided significantly higher energy density compared to earlier technologies, enabling smartphones to perform more complex tasks for extended periods. This technological synergy between miniaturization and battery advancement led to the creation of the portable, powerful devices we use today.
Processing Power and Software
The development of powerful and efficient processors, coupled with advancements in mobile operating systems, significantly impacted smartphone capabilities. Early smartphones often relied on limited processing power, resulting in slower application performance and reduced responsiveness. Improvements in processor architecture and design allowed for more complex tasks to be handled seamlessly, such as running multiple applications simultaneously or handling demanding graphic-intensive games.
This evolution was further facilitated by the development of optimized operating systems like Android and iOS, designed to efficiently manage resources and provide a smooth user experience. This symbiotic relationship between hardware and software has propelled the smartphone into its position as a versatile computing platform.
Impact on Society and Culture
The widespread adoption of smartphones has profoundly reshaped society and culture, altering communication patterns, information access, and economic landscapes. This pervasive technology has become an indispensable tool, impacting nearly every facet of modern life, from personal relationships to global commerce.The smartphone’s influence extends far beyond simply facilitating communication. It has fostered a new era of interconnectedness, blurring geographical boundaries and creating unprecedented opportunities for social interaction and knowledge sharing.
However, this transformation has also presented new challenges and considerations, prompting ongoing discussions about its impact on privacy, mental health, and the very nature of human connection.
Transformation of Communication
The smartphone revolutionized communication by introducing instant messaging, video calls, and social media platforms. These tools have fundamentally changed how individuals interact, fostering new forms of community and social organization. Prior to smartphones, communication was often limited by time and distance, requiring dedicated phone calls or lengthy mail correspondence. Now, instant communication is ubiquitous, enabling immediate responses and global connections.
Information Access and Consumption
Smartphones have dramatically expanded access to information, placing a vast library of knowledge at the fingertips of users. News, research articles, and educational resources are readily available, empowering individuals to stay informed and learn continuously. This accessibility has also fostered a new dynamic in how information is consumed, leading to a faster pace of news dissemination and a constant stream of updates.
Users can now access real-time information, creating a sense of immediacy and connectivity to events worldwide.
Economic Effects, When were smartphones invented
The smartphone revolution has had a profound economic impact, creating new industries, jobs, and business models. Mobile commerce (m-commerce) has surged, enabling consumers to make purchases and conduct transactions directly from their devices. This shift has created new opportunities for businesses to reach wider audiences and connect directly with customers. Furthermore, the development and maintenance of smartphone applications (apps) have generated numerous jobs in software development, design, and marketing.
Changing Communication Habits
| Communication Method | Pre-Smartphone Era | Smartphone Era |
|---|---|---|
| Face-to-Face Interactions | Predominant mode of personal communication. | Still crucial, but often supplemented by virtual interactions. |
| Phone Calls | Primary means of long-distance communication. | Still used, but increasingly supplemented by video calls and messaging. |
| Letters/Mail | Common method for formal communication. | Rarely used for formal communication; primarily for personal notes or sentimental purposes. |
| Information Gathering | Libraries, newspapers, and specialized databases. | Online search engines, mobile news apps, and dedicated information platforms. |
| Social Interaction | Limited to local communities and in-person gatherings. | Global reach through social media, enabling broader social connections. |
The table above highlights a stark contrast in communication patterns before and after the smartphone era. The smartphone has undeniably transformed the way we communicate and access information. It’s important to recognize that these shifts are not merely technological upgrades but fundamental changes in how society functions.
Smartphones, as we know them, really took off around the late 2000s. The rapid evolution of technology, coupled with the innovative concepts like the “paperlike smartphone” ( paperlike smartphone ), have fundamentally changed how we interact with the digital world. However, the precise invention dates of early prototypes are a bit more murky.
Evolution of Mobile Operating Systems

The development of mobile operating systems has been instrumental in shaping the smartphone landscape. From simple interfaces to complex ecosystems, these systems have evolved alongside the hardware, impacting user experience and market dynamics. This evolution reflects the ever-increasing demand for sophisticated functionalities and seamless integration with other technologies.The initial mobile operating systems were largely limited in functionality and application diversity.
As technology advanced, a race for innovation ensued, with different platforms vying for market dominance. This competition spurred significant improvements in user interface design, application development, and overall user experience.
Key Mobile Operating Systems
Various mobile operating systems have emerged, each with its unique characteristics and strengths. The most prominent players include iOS and Android, each holding a substantial market share. Other platforms, such as Blackberry OS and Windows Phone, have also left their mark, though their presence has diminished. Understanding the evolution of these systems offers valuable insights into the historical trajectory of the smartphone industry.
iOS
Apple’s iOS, initially developed for the iPhone, has consistently focused on a user-friendly interface and a tightly integrated ecosystem. Its early iterations prioritized simplicity and ease of use, while later versions introduced advanced features such as multitasking and app store integration. This approach emphasized user experience and created a loyal user base.
Android
Google’s Android, open-source and highly customizable, rapidly gained popularity due to its adaptability and extensive developer community. Early Android versions often suffered from inconsistencies in user experience, but subsequent iterations addressed these issues and expanded the platform’s functionality. The open-source nature attracted a large developer base, leading to a vast array of applications and devices.
Comparison of iOS and Android
| Feature | iOS | Android |
|---|---|---|
| User Interface | Intuitive, streamlined design, consistent user experience. | Customizable, diverse design across manufacturers, potentially less consistent. |
| Ecosystem | Tightly integrated hardware and software, limited third-party options. | Open ecosystem, allowing for diverse hardware choices and extensive third-party apps. |
| Customization | Limited customization options. | Highly customizable, enabling user modification of appearance and functionality. |
| App Store | App Store with a focus on quality and vetting. | Google Play Store, offering a vast selection of apps. |
The table above highlights key distinctions between the two leading mobile operating systems. These differences have significantly impacted the market, influencing consumer choices and developer strategies.
Development of Other Operating Systems
Other notable mobile operating systems include BlackBerry OS, known for its robust email capabilities, and Windows Phone, focused on integration with Microsoft’s ecosystem. While these platforms held a presence in the market, they have since declined in prominence due to factors such as evolving market demands and competition from iOS and Android.
Impact on Market
The dominance of iOS and Android has shaped the smartphone market, influencing hardware design, application development, and user expectations. The sheer number of apps available on Android, combined with the customization options, attracted a vast user base. iOS’s focus on a premium user experience and seamless integration led to a high-end market segment.
Market Trends and Competition: When Were Smartphones Invented
The smartphone market’s evolution has been profoundly shaped by a dynamic interplay of technological advancements and fierce competition. Emerging trends, like the rising demand for mobile internet access and increasing consumer expectations for sophisticated devices, have driven innovation. Understanding these trends and the competitive landscape is crucial to appreciating the intricate path of smartphone development.The intense rivalry among manufacturers has spurred rapid advancements in processing power, camera technology, and display quality.
This constant pressure to outperform rivals has translated into a relentless cycle of innovation, ultimately benefiting consumers.
Major Market Trends
The evolution of smartphones has been profoundly influenced by several key market trends. These trends include a rising demand for mobile internet access, fuelled by the proliferation of affordable data plans and the increasing need for connectivity on the go. Simultaneously, there’s been a growing desire for sophisticated devices with a multitude of functions, moving beyond basic communication to encompass entertainment, productivity, and social interaction.
Competition Between Manufacturers
The smartphone market is characterized by intense competition among numerous manufacturers. Apple, Samsung, and Google, among others, have consistently engaged in a battle for market share, driving innovation and shaping consumer expectations. This competition has been particularly visible in the relentless pursuit of superior hardware, software, and design features.
Summary of Emerging Models and Brands
The smartphone market has witnessed the emergence of numerous models and brands over the years. Early entrants like Nokia and BlackBerry faced challenges adapting to evolving market demands, while newcomers, like OnePlus and Xiaomi, have successfully carved out niches. This diversification has led to a wide array of choices for consumers, catering to different budgets and preferences.
Chronological Table of Smartphone Manufacturers and Product Releases
| Manufacturer | Product Release Year | Key Features/Models |
|---|---|---|
| Nokia | 2000s | Early mobile phones with limited internet access, including the iconic 3310. |
| Apple | 2007 | iPhone, introducing a touch-screen interface and app store. |
| Samsung | 2008 | Galaxy series, emphasizing affordability and user-friendly design. |
| BlackBerry | 2000s-2010s | Popular for their keyboards and email functionality. |
| Motorola | 2000s | Early entrants with notable models like the Razr. |
| 2008 | Android OS, enabling diverse manufacturers to enter the market. | |
| OnePlus | 2013 | High-performance devices at competitive price points. |
| Xiaomi | 2010 | Affordable smartphones with increasing specifications. |
| Huawei | 2000s-present | Significant competitor globally, offering a wide range of models. |
Global Adoption and Distribution
Smartphone adoption has been a remarkably rapid and widespread phenomenon, transforming societies across the globe. This global diffusion has been driven by a complex interplay of factors, ranging from economic development to technological advancements and evolving consumer preferences. Understanding the patterns of adoption and the strategies employed by manufacturers and distributors is crucial to appreciating the transformative impact of smartphones.
Global Adoption Rates
Smartphone penetration varies significantly across different regions. Developed nations, such as those in North America and Western Europe, often exhibit higher adoption rates due to factors like higher disposable incomes and a greater awareness of mobile technology. Conversely, developing countries, particularly in sub-Saharan Africa and parts of Asia, are experiencing rapid growth in smartphone adoption as mobile networks expand and prices decrease.
This disparity in adoption rates reflects the diverse economic landscapes and technological infrastructure across the globe.
Factors Influencing Adoption
Several factors contribute to the varying levels of smartphone adoption across countries. Economic conditions play a crucial role; higher disposable incomes generally correlate with increased smartphone ownership. The availability and affordability of mobile data plans are also significant; reliable and affordable internet access is a key driver for smartphone use. Furthermore, government policies, such as subsidies for mobile devices, can encourage adoption in specific regions.
Cultural acceptance of mobile technology, along with educational levels, further influence smartphone penetration. A general understanding of mobile technologies and internet access further fuels the demand for smartphones.
Distribution Channels
The success of smartphone distribution hinges on a variety of channels. Retailers, including large multinational corporations and local shops, play a critical role in making smartphones accessible to consumers. Online marketplaces, such as e-commerce platforms, are increasingly important for reaching a wider audience and providing competitive pricing. Mobile network providers often partner with manufacturers to offer bundled deals, making smartphones more attractive to customers.
Finally, grey markets, while sometimes controversial, can provide access to devices at lower costs, potentially accelerating adoption in regions with limited formal retail options.
High Smartphone Penetration Regions
The regions with the highest smartphone penetration typically align with developed economies and regions with robust mobile infrastructure. North America, Western Europe, and parts of East Asia consistently demonstrate high adoption rates. These areas frequently display a convergence of factors, including robust economies, advanced telecommunications networks, and widespread consumer acceptance of technology. A visualization of this could be represented on a world map, highlighting the differing levels of smartphone penetration across various continents and countries.
Future Trends and Innovations

The smartphone landscape is constantly evolving, driven by relentless innovation and user demand. Emerging technologies are poised to reshape the mobile experience, offering enhanced capabilities and impacting various facets of society. This section explores the key future trends and potential innovations shaping the future of mobile technology.
Beyond the Screen: Augmented and Virtual Reality
Immersive technologies like augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) are rapidly integrating into smartphones. AR overlays digital information onto the real world, enhancing user interaction with physical environments, while VR transports users to entirely simulated realities. These advancements are expected to revolutionize gaming, education, and entertainment, creating novel and interactive experiences. For example, AR filters and overlays are becoming increasingly common in social media applications, and VR gaming experiences are already providing compelling alternatives to traditional forms of entertainment.
Early adoption of AR and VR features in smartphones signifies a potential paradigm shift in how we interact with and perceive the world around us.
Personalized Experiences: AI and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are transforming how smartphones adapt to individual user needs. AI-powered personalization is enabling customized recommendations for content, services, and applications. Sophisticated algorithms learn user preferences, optimizing the user experience and anticipating needs. This trend is also leading to the development of more intelligent assistants, providing personalized information and services. Examples include personalized news feeds, tailored shopping recommendations, and adaptive learning tools.
These advancements will likely lead to more intuitive and relevant interactions between users and their devices.
Sustainable Technologies: Eco-Conscious Design
Growing environmental concerns are driving the development of more sustainable practices in the smartphone industry. This includes the use of recycled materials in manufacturing, the implementation of energy-efficient components, and the development of more sustainable charging solutions. The goal is to reduce the environmental impact of smartphone production and usage. Companies are increasingly emphasizing the lifecycle of their products, incorporating design features that promote reusability and repairability.
This eco-conscious approach to mobile technology is gaining traction and is expected to be a significant factor in future smartphone development.
Smartphones, as we know them, really took off around the late 2000s. Figuring out how to connect your phone to your laptop without Wi-Fi can be tricky, though. Fortunately, there are plenty of solutions, like using a USB cable or Bluetooth, and you can find detailed instructions on how to connect a smartphone to a laptop without Wi-Fi here.
Ultimately, the invention of smartphones has revolutionized communication and computing, leading to the ubiquitous devices we use today.
Connectivity and Network Innovations
The need for faster and more reliable connectivity continues to drive innovation in mobile networks. 5G technology is already transforming communication and data transfer speeds, enabling a wider range of applications, such as real-time video streaming and advanced gaming experiences. The next generation of mobile networks is anticipated to offer even higher bandwidth and lower latency, furthering the integration of mobile devices into diverse sectors.
Continued development in 6G and beyond is expected to enable more seamless and responsive connectivity.
Security and Privacy Enhancements
Security and privacy concerns are paramount in the evolution of smartphones. Future trends will focus on enhanced security measures, including biometric authentication, secure data encryption, and advanced threat detection mechanisms. Users will likely demand more transparency and control over their personal data, prompting the development of more user-friendly privacy settings and features. This will be crucial in maintaining user trust and ensuring the secure use of mobile devices.
Potential Future Innovations in Smartphones
- Self-Repairing Smartphones: Incorporating self-healing materials or mechanisms to extend the lifespan of the device.
- Transparent Displays: Utilizing flexible, transparent displays for innovative interaction and augmented reality experiences.
- Brain-Computer Interfaces: Integrating direct communication between the brain and the smartphone, enabling intuitive control and interaction.
- Biometric Authentication beyond Fingerprints: Utilizing more advanced biometric methods, such as facial recognition and eye scanning, for enhanced security.
- Personalized Health Monitoring: Employing advanced sensors and AI to provide detailed health insights and personalized recommendations for wellness.
Specific Models and Brands
The evolution of smartphones is intrinsically linked to the innovative models and brands that pushed the boundaries of technology and design. These models, each representing a significant leap forward, captivated consumers and reshaped the industry. From early iterations to modern marvels, the journey reflects the constant drive for improved performance, aesthetics, and user experience.Specific models and brands played a crucial role in defining the smartphone landscape, impacting both technological advancements and consumer adoption.
Key models often introduced groundbreaking features that spurred competition and further innovation.
Influential Smartphone Models by Brand
A multitude of models from various brands have left their mark on the smartphone market. This section explores some pivotal models that significantly influenced the smartphone evolution.
- Apple iPhone: The iPhone, introduced in 2007, revolutionized the smartphone experience. Its touch-screen interface, integrated media player, and intuitive software design were unprecedented in the mobile market. The iPhone set a new standard for user experience and sparked a surge in smartphone adoption. Subsequent models like the iPhone 3G and 4 further solidified Apple’s position in the market by introducing features such as 3G connectivity and advanced cameras.
- Samsung Galaxy: The Samsung Galaxy S series emerged as a major competitor to the iPhone. The Galaxy S3, for instance, highlighted Samsung’s focus on processing power and user interface enhancements, presenting a compelling alternative to Apple’s offerings. The introduction of the Galaxy S series expanded the range of smartphone choices and drove innovation in terms of display size and camera capabilities.
- Nokia 3310: While not necessarily a flagship model in terms of features, the Nokia 3310 stands out for its remarkable resilience and affordability. Its simplicity and robust design appealed to a large user base, particularly in developing regions. The enduring popularity of the 3310 showcases the importance of affordability and reliability in the smartphone market, demonstrating that basic features can still hold significant appeal.
This model showcased a balance between affordability and usability, a key factor in the initial widespread adoption of mobile phones.
- Motorola Razr: The Motorola Razr, a clamshell phone released in 2004, showcased a unique design that became a recognizable symbol of mobile technology. Its compact form factor, coupled with some advanced features for the time, reflected a desire for portability and stylish design. The Razr, though not a defining force in the smartphone era, demonstrates an early interest in form factor as a critical selling point.
Key Innovations Across Smartphone Models
The evolution of smartphone models is closely tied to advancements in various technologies. Here’s a glimpse into some of the key innovations that shaped the evolution:
- Display Technology: The transition from small, monochrome displays to vibrant, high-resolution color screens significantly enhanced the user experience. The increasing screen sizes, coupled with advancements in resolution and touch responsiveness, made smartphones more engaging and versatile.
- Processing Power: Increased processing power enabled more complex applications and smoother multitasking. This progress led to a more responsive and engaging user experience. The rise of multi-core processors further enhanced performance and enabled the execution of demanding applications.
- Camera Technology: The inclusion of advanced cameras in smartphones transformed how users capture and share images and videos. The gradual improvements in sensor technology, image processing, and video recording capabilities have become a defining feature of modern smartphones.
Influential Brands in Shaping the Market
Beyond specific models, certain brands played pivotal roles in shaping the smartphone market.
- Apple: Apple’s focus on user experience and design aesthetics has consistently influenced the market, setting high standards for other brands to emulate.
- Samsung: Samsung’s aggressive approach to competing with Apple has driven innovation and diversification in the market, offering a wider range of options to consumers.
- Google: Google’s Android operating system has become a dominant force in the global smartphone market, driving competition and influencing the software landscape.
Conclusive Thoughts
In conclusion, the journey from the initial concept to the ubiquitous smartphone reflects remarkable technological progress and its profound impact on our lives. From the key individuals and companies to the global adoption rates, this history underscores the transformative power of innovation. The future of mobile technology holds exciting possibilities, and the story of smartphones continues to unfold.
Top FAQs
What was the first commercially successful smartphone?
The first commercially successful smartphone is generally considered to be the Apple iPhone.
What are the key differences between smartphones and feature phones?
Smartphones offer advanced computing capabilities, internet access, and app downloads, whereas feature phones are primarily for calling and texting.
How did the development of touchscreens impact smartphones?
Touchscreens revolutionized smartphone interaction, making them more intuitive and user-friendly compared to earlier keypad-based devices.
What role did mobile internet connectivity play in the rise of smartphones?
Mobile internet connectivity provided access to the wider world of information and applications, enabling smartphones to become more than just communication devices.





