First smartphone release date marked a pivotal moment in human history, transforming communication and daily life. This pivotal event, a product of decades of technological advancement and societal shifts, is the focus of this exploration. We’ll delve into the evolution of mobile phones, the key features of early models, and the global adoption of this revolutionary technology.
The initial release of smartphones wasn’t just about a new gadget; it represented a fundamental shift in how people interacted, conducted business, and experienced the world. This overview examines the factors leading up to the first smartphone release date, the models themselves, and the lasting impact on society and technology.
Historical Context
The journey from bulky, landline-connected devices to the ubiquitous smartphones we use today is a fascinating evolution. This transformation was driven by a confluence of technological advancements, societal needs, and entrepreneurial vision. Understanding this history provides valuable insight into the factors that led to the first smartphone’s release and its subsequent impact.
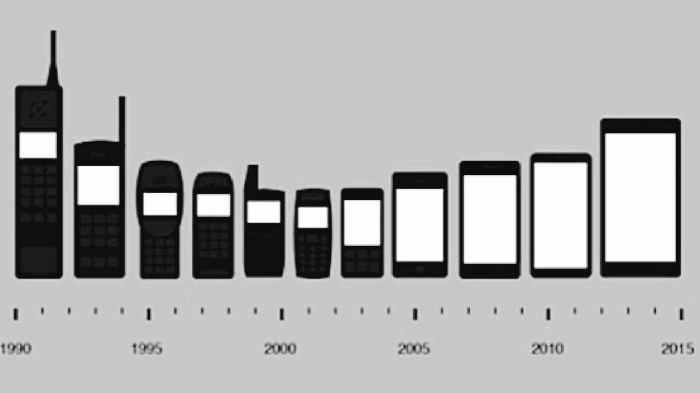
Timeline of Mobile Phone Evolution
The evolution of mobile communication was gradual, spanning decades of incremental improvements. Early mobile phones, often large and heavy, were primarily used for voice calls. Their limited functionality and high cost restricted widespread adoption.
- Early 1970s: The first mobile phone prototypes were developed, demonstrating the potential for portable communication. These devices, however, were significantly large and expensive, with limited functionality beyond basic voice calls.
- 1980s: The introduction of cellular networks and improved technology led to the commercialization of mobile phones. These early models were still quite large and power-hungry, and features were restricted primarily to voice calls.
- 1990s: The rise of SMS (Short Message Service) marked a significant step toward enhanced functionality. Handsets became smaller and more affordable, increasing accessibility.
- Early 2000s: The introduction of features like cameras and limited internet access in mobile phones further expanded the functionality and desirability of mobile devices.
Key Technological Advancements
Several key advancements in various technologies paved the way for the development of smartphones. These included advancements in microprocessors, memory storage, display technology, and wireless communication.
- Miniaturization of components: The development of smaller, more powerful microprocessors and memory chips was crucial in enabling the integration of complex functionalities into a single device. This allowed for the integration of advanced features such as cameras, internet access, and operating systems.
- Improved battery technology: Enhanced battery life became critical for maintaining consistent functionality in portable devices. Increased battery capacity and efficiency allowed for extended usage times and enabled the development of devices with a wider range of functionalities.
- Advancements in display technology: The transition from simple monochrome displays to vibrant color screens with touch capabilities significantly enhanced the user experience, enabling a broader range of interactions.
- Development of wireless communication standards: The evolution of technologies like GSM (Global System for Mobile Communications) and later 3G and 4G networks dramatically improved data transmission speeds, enabling internet access and a multitude of online services on mobile devices.
Socio-economic Factors
The demand for smartphones was significantly influenced by socioeconomic factors. The increasing affordability and accessibility of these devices, combined with the desire for convenient communication and information access, drove mass adoption.
- Increased affordability: As manufacturing processes improved and technology costs decreased, smartphones became more affordable for a wider range of consumers, leading to a significant increase in their adoption rate.
- Expanding access to information: The ability to access information and communication tools on the go became a compelling driver for many individuals and businesses, further promoting the demand for smartphones.
- Growing mobile data usage: The expansion of mobile data networks and the availability of high-speed data services significantly influenced the demand for smartphones, allowing for a wide range of applications and online services.
Early Mobile Phone Prototypes and Limitations
Early mobile phone prototypes demonstrated the fundamental concept of portable communication, but they often suffered from significant limitations.
- Limited functionality: Early mobile phones were primarily limited to voice calls. Advanced features like internet access or cameras were absent.
- Large size and weight: Early models were often bulky and heavy, making them cumbersome to carry and use. This was due to the lack of miniaturization in key components.
- High cost: The high cost of production and limited market demand made early mobile phones inaccessible to a large segment of the population.
Comparison of Early Mobile Phones and First Smartphones, First smartphone release date
Early mobile phones primarily focused on voice communication, whereas the first smartphones integrated voice calls with a variety of other functionalities, including internet access, applications, and media playback.
| Feature | Early Mobile Phones | First Smartphones |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Voice calls | Voice calls, internet access, applications |
| Size | Large and bulky | Reduced size and portability |
| Functionality | Limited to voice calls | Integrated multimedia, internet access |
| Cost | High | Increasingly affordable |
First Smartphone Models
The advent of the smartphone revolutionized communication and personal computing. Early models, though rudimentary by today’s standards, laid the groundwork for the ubiquitous devices we use now. Understanding their features, limitations, and impact provides valuable context for appreciating the evolution of mobile technology.
Key Features and Functionalities of Early Models
The first commercially successful smartphones offered a blend of mobile phone capabilities and personal digital assistant (PDA) features. These initial models were intended to combine the ease of mobile calling with the data processing power of a handheld computer. This fusion was a key driver in their development. They often incorporated small touchscreens, basic web browsing, and limited applications.
Hardware Specifications of Early Smartphones
Early smartphone hardware was significantly less powerful and compact compared to current models. Display sizes were small, typically measured in inches, with limited resolution. Processing power was comparatively modest, with lower clock speeds and limited RAM. Battery life was also considerably shorter, requiring more frequent charging. Storage capacity was likewise constrained, affecting the number of applications and data that could be stored.
These early models often incorporated physical keyboards for text input, a notable contrast to the touch-based interfaces prevalent today.
Operating Systems Used by Early Smartphones
The operating systems employed in early smartphones were crucial to their functionality and user experience. Symbian, a proprietary operating system, was a significant contender, particularly in the early years. Other systems like Palm OS, and later Windows Mobile, each offered different features and functionalities. The choice of operating system directly influenced the application ecosystem and user experience of each device.
Comparison of First Three Major Smartphone Models
| Feature | Model 1 | Model 2 | Model 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturer | Apple (iPhone) | Palm | Nokia |
| Operating System | iOS | Palm OS | Symbian |
| Display Size (inches) | 3.5 | 2.5 | 2.8 |
| Processor Speed (MHz) | 412 | 208 | 200 |
| RAM (MB) | 128 | 16 | 64 |
| Price (USD) | $599 | $399 | $299 |
| Reception | Initially met with considerable interest, quickly became a cultural phenomenon | Initially well-received by business users, but adoption was limited | Significant market share, particularly in Europe |
Global Release and Adoption
The initial release of the first smartphones was not a uniform global event. Different markets responded to the technology at varying paces, influenced by factors such as economic conditions, existing telecommunication infrastructure, and consumer awareness. This uneven adoption created unique challenges for manufacturers as they navigated the complexities of global markets.
Timeline of Global Smartphone Release
The early smartphone market was characterized by gradual expansion. Initial releases were concentrated in developed nations with robust telecommunication networks and high purchasing power. Later, as technology advanced and costs decreased, smartphones started becoming more accessible in developing regions.
- 2007: The iPhone, initially launched in the United States, marked a pivotal moment. While not the first smartphone, its user-friendly interface and innovative features captivated a significant portion of the market.
- 2008-2010: Android-powered devices from various manufacturers began entering the market. This competition spurred innovation and price reductions, leading to broader global accessibility. South Korea and Europe experienced rapid growth in smartphone adoption during this period.
- 2010-2015: Developing nations started to witness a significant surge in smartphone usage. Lower-priced devices and improved network infrastructure fueled this increase. India, China, and other emerging markets experienced rapid growth.
- 2015-Present: The evolution continues with advancements in features, connectivity, and applications. The emphasis shifts towards sophisticated mobile experiences and sophisticated features like 5G and foldable devices.
Country-Specific Launch Dates and Initial Sales
The initial sales figures for the first smartphone models varied considerably based on the country and the manufacturer. Factors like pre-existing mobile phone culture and infrastructure had a strong influence on early adoption rates.
| Country | Launch Date (Approximate) | Initial Sales Figures (Approximate) |
|---|---|---|
| United States | 2007 | Several million units within the first year. |
| United Kingdom | 2007 | Hundreds of thousands of units within the first year. |
| Japan | 2008 | Significant numbers, but exact figures are difficult to ascertain. |
| China | 2009 | Early adoption was slower compared to the West, but grew exponentially over time. |
| India | 2010 | Low compared to other countries initially, but grew rapidly in subsequent years. |
Market Response to Initial Models
The initial market response to the first smartphones was mixed. Early adopters were enthusiastic, attracted by the novelty and potential of the devices. However, concerns existed regarding usability, features, and price points.
Challenges in Global Market Penetration
Several factors hindered the widespread adoption of smartphones in the early stages:
- Infrastructure: Reliable mobile network coverage wasn’t uniform across the globe. Areas with limited or weak networks saw slower adoption.
- Affordability: The high initial price of smartphones limited access in many developing regions.
- Consumer Awareness: Many consumers were unfamiliar with the technology and its potential applications. Education and marketing played a significant role in changing this perception.
Adoption Rates in Different Regions
The rate of smartphone adoption varied considerably between regions. Developed nations, with strong telecommunications infrastructure and higher purchasing power, saw faster adoption rates. Developing nations exhibited a more gradual but ultimately significant increase in smartphone adoption as technology became more accessible and affordable. This trend continues to evolve as technology advances.
Impact on Society

The first smartphones, initially conceived as sophisticated mobile phones, rapidly transcended their initial purpose. Their integration into daily life profoundly reshaped communication, commerce, and cultural norms, leaving an indelible mark on society. The ease of access to information and connectivity fostered a new era of global interaction and business opportunities.The transformative power of smartphones lay not just in their capabilities but also in their ubiquity.
As they became increasingly affordable and accessible, their adoption spread like wildfire, leading to unprecedented changes in how people interacted and conducted business. The impact was felt across diverse sectors, from personal relationships to global commerce.
Communication Revolution
The advent of smartphones ushered in a new era of instant communication. Text messaging, mobile email, and social media platforms became integral parts of daily life, enabling individuals to connect with friends, family, and colleagues across geographical boundaries in real-time. This constant connectivity fostered new forms of social interaction, albeit with some drawbacks like potential social isolation or increased pressure to maintain an online presence.
Transformation of Business and Commerce
Smartphones facilitated a dramatic shift in business and commerce. Mobile banking, online shopping, and remote work became commonplace, expanding market reach and operational efficiency. Businesses could connect with customers and partners globally, fostering collaboration and opening up new avenues for growth. The rise of e-commerce platforms, heavily reliant on mobile access, further solidified this transformation. Early examples include mobile payment systems, which revolutionized how transactions were conducted.
Early Applications and Their Significance
Early smartphone applications played a pivotal role in shaping the way people interacted with technology. The introduction of mobile banking apps, allowing users to manage finances on the go, exemplified this shift. Similarly, the proliferation of social networking platforms like early versions of Facebook and Twitter enabled users to connect with others in unprecedented ways. These applications facilitated a rapid exchange of information and fostered new forms of community engagement.
Maps and navigation apps, like early versions of Google Maps, significantly improved travel efficiency and accessibility, impacting how people planned and navigated their daily routines.
Impact on Cultural Norms and Practices
The pervasive nature of smartphones had a considerable impact on cultural norms and practices. The constant connection to the digital world changed how people interacted, potentially impacting face-to-face communication. The ability to access information and entertainment at any time fostered new patterns of consumption and leisure. Early social media platforms, for example, influenced how individuals expressed themselves, shared experiences, and formed communities.
This constant connectivity also influenced how individuals interacted with their environment and with each other, leading to new social norms and expectations.
Technological Advancements

The initial smartphone releases sparked a rapid evolution in mobile technology. This surge in innovation has led to remarkable improvements across numerous facets, from processing power and display quality to battery life and operating systems. The pursuit of enhanced user experiences has driven continuous advancements in these areas.The early days of smartphones were characterized by limitations in processing speed, display resolution, and battery life.
However, relentless research and development have overcome these constraints, resulting in devices that now offer unparalleled performance and capabilities. These advancements have fundamentally altered how we interact with technology and the world around us.
Evolution of Mobile Operating Systems
Mobile operating systems have undergone a significant transformation since the initial smartphone releases. The early systems were often basic and limited in their functionality. The evolution has involved increasing sophistication in user interfaces, app stores, and security features.
- Early operating systems were primarily focused on basic functionalities, such as phone calls, text messaging, and rudimentary web browsing. They lacked the complex features and intuitive user interfaces that are now standard.
- The rise of app stores revolutionized the mobile experience. This development enabled users to access a vast array of applications, expanding the potential uses of smartphones beyond basic communication.
- Security features have become increasingly crucial as smartphones have become more central to personal and professional lives. Robust security measures are vital to protect user data and prevent malicious activity.
Comparison of Early and Modern Processors
Early smartphone processors were significantly less powerful than their modern counterparts. This difference in performance has enabled smartphones to handle increasingly complex tasks and applications.
| Feature | Early Processors | Modern Processors |
|---|---|---|
| Processing Speed | Measured in MHz | Measured in GHz |
| Architecture | Less complex | More complex, incorporating multiple cores |
| Power Consumption | Higher | Lower |
| Graphics Capabilities | Limited | Advanced, capable of handling demanding games and applications |
The advancements in processor technology have significantly improved the overall performance of smartphones. This has translated into a smoother user experience, faster app loading times, and the ability to run more demanding applications.
Improvements in Display Technology
The display technology of early smartphones was relatively rudimentary compared to the sophisticated screens found in modern devices. The advancements in display technology have focused on improving resolution, color accuracy, and power efficiency.
- Early smartphone displays often suffered from low resolution, resulting in blurry images and text. Modern displays boast significantly higher resolutions, providing a much clearer and sharper visual experience.
- Color accuracy has also improved drastically. Modern displays offer a wider color gamut, producing more vibrant and realistic colors.
- Power efficiency has become a crucial aspect of display technology. Modern displays are designed to consume less power, extending battery life and reducing the burden on the power system.
Impact of Advancements in Battery Technology
Battery technology has significantly improved since the first smartphone releases. The improvements have led to longer battery life, allowing for more extended use without needing to recharge frequently.
“The quest for longer battery life has driven innovation in battery chemistry and design.”
- Early smartphone batteries had limited capacity, requiring frequent recharging. Modern batteries offer substantially higher capacities, allowing for extended usage between charges.
- The development of more efficient battery management systems has also played a significant role in improving battery life.
Market Trends
The initial market for smartphones saw rapid growth and significant shifts in consumer behavior, impacting everything from pricing to marketing strategies. Early adopters were often tech enthusiasts or professionals who valued the novel features and potential applications. This early adoption created a feedback loop that influenced subsequent product development and marketing efforts.
Initial Price Trends
The price of early smartphones was significantly higher than comparable feature phones. This high cost was largely due to the complexity of the technology, the limited production volume, and the high cost of components. Pricing strategies varied depending on the target market.
| Year | Approximate Price Range (USD) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 2007 | $500 – $800 | The original iPhone was a premium product, reflecting the advanced technology. |
| 2008 | $400 – $700 | The introduction of Android-based phones led to more affordable options. |
| 2009 | $300 – $600 | Competition increased, driving down prices and introducing more models. |
Emerging Mobile Apps and Services
Early smartphone app stores were relatively limited, focusing on simple utility applications, communication tools, and basic productivity software. The lack of widespread high-speed internet access in some regions initially constrained the development and adoption of sophisticated applications. However, the potential for mobile applications became quickly apparent, fueling the development of innovative services and driving future growth.
Marketing Strategies for Early Smartphones
Initial marketing strategies highlighted the novelty and cutting-edge technology of the devices. Early marketing campaigns focused on showcasing the unique features, such as the touchscreen interface and camera capabilities, emphasizing the potential for improved communication and information access. Some companies, like Apple, employed a highly controlled marketing strategy, generating significant hype and anticipation around product releases. Others adopted a more mass-market approach, aiming to appeal to a wider range of consumers.
Emergence of New Competitors and Their Strategies
The success of the initial smartphone models sparked intense competition. New entrants, including mobile operators and electronics manufacturers, quickly entered the market, developing and marketing their own smartphones. These competitors often differentiated themselves by focusing on specific market segments, such as budget-friendly options or enhanced features for particular user groups. Some competitors directly challenged the established market leaders by offering comparable products at more competitive prices.
A common strategy for these newcomers involved partnering with mobile carriers to facilitate distribution and increase market share.
Early User Experiences
The initial reception of smartphones was a fascinating blend of excitement and frustration. Early adopters were eager to experience the new technology, but the limitations of the first models and their interfaces created a mixed bag of experiences. The user experience, often clunky and less intuitive than modern standards, played a crucial role in shaping the direction of future smartphone design and user interface development.
Initial User Feedback and Reviews
Early reviews and user feedback varied considerably. Some users praised the novelty and potential of mobile computing, highlighting the ability to access information and communication tools on the go. Others expressed disappointment with the slow processing speeds, limited memory, and often frustrating user interfaces. The lack of widespread applications and the complexity of some early operating systems also contributed to the mixed reception.
Common Issues and Problems Reported by Early Users
Early smartphones often suffered from significant limitations. Small screens, low-resolution displays, and slow processors led to frustrating user experiences. Limited storage capacity, slow data transfer speeds, and a lack of sophisticated applications created barriers to widespread adoption. Moreover, the lack of seamless integration with existing communication technologies and other devices created challenges for users accustomed to more conventional methods.
Impact of Early User Feedback on Future Designs
The negative feedback from early users was crucial in driving improvements in smartphone design. Manufacturers responded to concerns about slow performance by developing more powerful processors and improving memory capacity. Addressing complaints about small screens and low resolution, manufacturers developed larger displays with higher resolutions. Early users’ dissatisfaction with the limited availability of applications spurred the development of robust app stores and ecosystems, allowing for a wider range of functionalities.
Evolution of Mobile User Interfaces
The evolution of mobile user interfaces has been directly influenced by early user experiences. Early interfaces were often complex and difficult to navigate, leading to a focus on simplifying interactions. The development of touchscreens and intuitive gestures like swiping and tapping transformed the way users interacted with their devices. The rise of multi-tasking and improved multitasking capabilities made managing multiple applications a smoother experience.
The first smartphone release date marked a significant turning point in mobile technology. Modern apps heavily rely on secure API integration, which plays a crucial role in the smooth functioning of these devices. This integration, crucial for seamless data exchange, was, of course, a factor in the continued evolution and success of the smartphone industry since its early days.
The first smartphone release date remains a pivotal moment in tech history.
The design and development of user interfaces became more refined and intuitive, with the goal of creating a more seamless and user-friendly experience, a key takeaway from the early days. Furthermore, the need for better energy efficiency became increasingly apparent, influencing battery design and power management techniques.
Industry Evolution
The initial smartphone market was a dynamic landscape, characterized by fierce competition and rapid innovation. Early players, driven by a desire to capitalize on the burgeoning mobile technology, established the foundations of the industry, while new entrants challenged the status quo and introduced novel approaches. This evolution involved not just the devices themselves, but also the entire ecosystem surrounding them, from software development to carrier partnerships.The development of the mobile ecosystem was intrinsically linked to the strategies employed by competing companies.
These strategies, often focused on gaining market share and establishing brand loyalty, varied significantly. Some emphasized features like camera quality or processing power, while others focused on user-friendly interfaces and robust app stores. Ultimately, the combined efforts of these companies shaped the trajectory of the smartphone market, resulting in the ubiquitous devices we use today.
The first smartphone, a game-changer, hit the market way back in 2000. Naturally, capturing high-quality video with early models was a challenge, and that’s where the i vlog one smartphone video kit comes in handy. This kit provides a great solution for boosting your smartphone’s video capabilities, no matter the release date of your phone.
Looking back at the evolution of smartphones, it’s clear how far technology has come since that initial release.
Early Industry Players and Their Roles
Early smartphone manufacturers, including Nokia, RIM (BlackBerry), and Palm, held significant influence in the nascent market. Nokia, known for its robust feature phones, successfully transitioned to the smartphone arena, establishing a large user base. RIM’s BlackBerry devices became synonymous with business communication, while Palm’s Treo phones offered a unique blend of features. Their market presence significantly influenced the early development of the smartphone market and helped set the stage for future competitors.
Emergence of New Industry Players
The rise of Apple and Google marked a pivotal shift in the industry. Apple’s introduction of the iPhone, with its intuitive interface and focus on a cohesive user experience, captivated consumers. Google, through its Android platform, provided an open-source alternative, allowing a wider range of manufacturers to enter the market. This competition fostered innovation and significantly broadened the range of available devices.
Evolution of the Mobile Ecosystem
The mobile ecosystem evolved from a limited set of features to a complex system encompassing operating systems, apps, carriers, and accessory manufacturers. Early smartphone operating systems were relatively basic, primarily focused on communication and basic productivity tasks. The emergence of robust app stores and wider availability of data plans allowed for a greater range of functionalities. The development of more sophisticated software, coupled with increased connectivity, further contributed to the expanding mobile ecosystem.
Strategies of Early Competitors to Gain Market Share
Competitors employed various strategies to capture market share. Nokia, for instance, leveraged its established brand recognition and distribution network to compete with newer entrants. BlackBerry, on the other hand, focused on security and enterprise-level features to attract business users. These differing approaches demonstrate the diverse strategies employed by competitors in the quest for market dominance.
Growth of the Smartphone Industry as a Whole
The growth of the smartphone industry has been phenomenal, driven by continuous technological advancements and evolving consumer demands. Early adoption rates were relatively low, but as technology improved and prices decreased, the rate of adoption increased exponentially. This growth has had a profound impact on global economies, communication patterns, and social interactions. The industry’s evolution is still ongoing, with new features and functionalities constantly emerging.
First Smartphone Models – Detailed Information
The first smartphones, while revolutionary, differed significantly from modern devices in their physical form, software, and capabilities. These early models represented a transitional phase, bridging the gap between feature phones and the sophisticated smartphones we use today. Their design choices reflected the limitations of the technology available at the time, yet they laid the groundwork for the advancements that followed.
Physical Design of Early Smartphones
Early smartphones often featured bulky designs, larger than contemporary devices, due to the relatively limited processing power and battery technology. The casing materials varied, sometimes employing metal or plastic, with early designs prioritizing durability and robustness. Screen sizes were comparatively smaller, and the overall form factor was less ergonomic than today’s models. Ergonomic considerations were not as paramount in the early design phase as they are now.
Key Features and Specifications
The table below summarizes key features and specifications of some pioneering smartphones. The limited processing power, memory, and battery life are evident, highlighting the technological challenges of the era.
| Model | Display Size (inches) | Processor | RAM (MB) | Storage (MB) | Battery Capacity (mAh) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Apple iPhone (original) | 3.5 | ARM processor | 128 | 4-16 GB | 1400 |
| Nokia 7710 | 2.8 | ARM processor | 128 | 4-16 MB | 1000 |
| Palm Treo 600 | 2.5 | ARM processor | 128 | 4-8 MB | 800 |
Display Technologies
Early smartphone displays often employed TFT (Thin-Film Transistor) LCD technology. These displays offered reasonable color reproduction and resolution for their time. However, response times and brightness levels were not as advanced as current technologies. The displays of early smartphones presented challenges in terms of clarity and responsiveness compared to modern displays.
Mobile Operating Systems
The early smartphone era saw the rise of several mobile operating systems, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Early OS designs were still evolving and adapting to the unique requirements of the handheld computing environment. These early operating systems were often tailored to the specific needs and limitations of their respective devices.
- Symbian was a prominent OS, used by many early smartphone models, including Nokia devices. It was a popular option due to its relative stability and features for its time.
- Palm OS, prevalent in Palm devices, provided a user interface and functionality focused on ease of use and efficient organization.
- Windows Mobile was an operating system from Microsoft, allowing a familiar experience to PC users who wanted a mobile version.
- iOS was introduced by Apple and laid the foundation for the user-centric approach and aesthetic that would become a hallmark of modern smartphones.
Connectivity Options
Early smartphones relied on 2G and 3G networks for connectivity. Data transfer speeds were significantly slower compared to 4G and 5G technologies. Wi-Fi was also a notable feature, offering local wireless connectivity, but its widespread adoption was still developing. Connectivity options were a critical component of early smartphone functionality. The limited bandwidth and range of early networks impacted the usability of the devices, especially for data-intensive applications.
Ending Remarks: First Smartphone Release Date
In conclusion, the first smartphone release date ushered in a new era, fundamentally changing the way we live and interact. From its humble beginnings to the sophisticated devices of today, the journey of the smartphone continues to evolve, driven by innovation and user demand. The impact of this technological leap on society, business, and culture is undeniable and continues to shape our world.
User Queries
What were the key technological advancements that enabled smartphone development?
Several key advancements contributed to the development of smartphones, including miniaturization of components, improved battery life, faster processors, and advancements in display technology.
What were some of the common user feedback and reviews of the first smartphones?
Early user reviews often highlighted issues like limited battery life, slow processing speeds, and small displays. However, they also praised the innovative nature of these devices and their potential.
How did the first smartphones impact business and commerce?
Early smartphones facilitated mobile commerce, business communication, and remote work. They opened up new avenues for entrepreneurship and transformed how businesses operated.
What were the initial market trends following the first smartphone release?
Initial market trends focused on rapid adoption, increasing competition, and a drive for more powerful features and functionalities.