Healthcare mobile apps revolutionize how we access and manage our well-being. From telehealth consultations to personalized fitness tracking, these applications are reshaping the healthcare landscape, offering a more convenient and accessible approach to care.
This guide delves into the evolution, design principles, technological advancements, market trends, and ethical considerations surrounding healthcare mobile apps. It explores the various categories, including telehealth, mental health support, and fitness tracking, along with their key features and functionalities. The guide also examines the crucial aspects of user experience, data security, and the impact on healthcare delivery and outcomes.
Overview of Mobile Healthcare Applications
Mobile healthcare applications (mHealth apps) have dramatically reshaped how individuals access and manage their health information and care. From simple fitness trackers to complex telehealth platforms, these apps are constantly evolving, reflecting advancements in technology and healthcare needs. This evolution has been driven by factors like increasing smartphone penetration, growing awareness of preventative health, and a desire for greater patient empowerment.Mobile health applications offer a wide range of services, spanning various aspects of health management.
This includes but is not limited to providing access to health information, promoting healthy lifestyles, and facilitating remote patient care.
Evolution of Mobile Healthcare Applications
Mobile healthcare applications have evolved significantly over time, moving from basic health trackers to sophisticated platforms offering comprehensive care management solutions. Early apps focused primarily on fitness tracking and basic health information. Subsequent iterations have integrated more sophisticated features, including remote monitoring, telehealth consultations, and personalized health coaching. This progression is directly linked to technological advancements and the increasing demand for accessible and convenient healthcare options.
Categories of Mobile Healthcare Applications
Mobile health applications are categorized into various types, each serving a distinct purpose in the healthcare ecosystem. These categories include:
- Telehealth applications enable remote consultations, monitoring, and treatment with healthcare providers. These applications use video conferencing, messaging, and remote monitoring devices to provide healthcare services without requiring in-person visits. Examples include virtual doctor visits, chronic disease management programs, and mental health support groups.
- Mental health applications offer support, resources, and tools for individuals experiencing mental health challenges. These apps provide access to information, coping mechanisms, stress management techniques, and interactive exercises. Some apps offer guided meditation sessions, journaling prompts, and support groups for mental health conditions.
- Fitness tracking applications assist users in monitoring their physical activity, sleep patterns, and nutritional intake. These apps often integrate with wearable devices to collect data and provide personalized insights. These applications are often designed to encourage healthy habits and motivate users to achieve their fitness goals. Examples include apps that track steps, calories burned, heart rate, and sleep.
- Chronic disease management applications provide tools for individuals managing chronic conditions. These apps offer personalized reminders for medication, tracking of symptoms, and access to educational resources. They are tailored to conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, and asthma. For example, a diabetes management app may include glucose monitoring tools, personalized meal plans, and educational materials about diabetes management.
Key Features and Functionalities
Many mobile healthcare applications share common features and functionalities. These functionalities enhance the user experience and improve the efficacy of the app’s purpose. Key features often include:
- Data tracking and analysis: Apps often allow users to track various health metrics, including steps, heart rate, sleep, and blood pressure. This data can then be analyzed to provide personalized insights and recommendations.
- Personalized health plans: Many apps provide personalized health plans based on individual needs and goals. This may include personalized exercise routines, dietary recommendations, or medication reminders.
- Communication tools: Apps may incorporate messaging or video conferencing capabilities to facilitate communication between patients and healthcare providers or other users.
- Educational resources: Some apps provide access to educational resources, including articles, videos, and interactive tutorials, to enhance user knowledge about health conditions or preventive care.
Platforms and Availability
Mobile healthcare applications are typically available on both iOS and Android platforms, ensuring broad accessibility. Some applications may also be accessible via web browsers. This availability across platforms is crucial for maximizing reach and user engagement.
User Experience and Interface Design
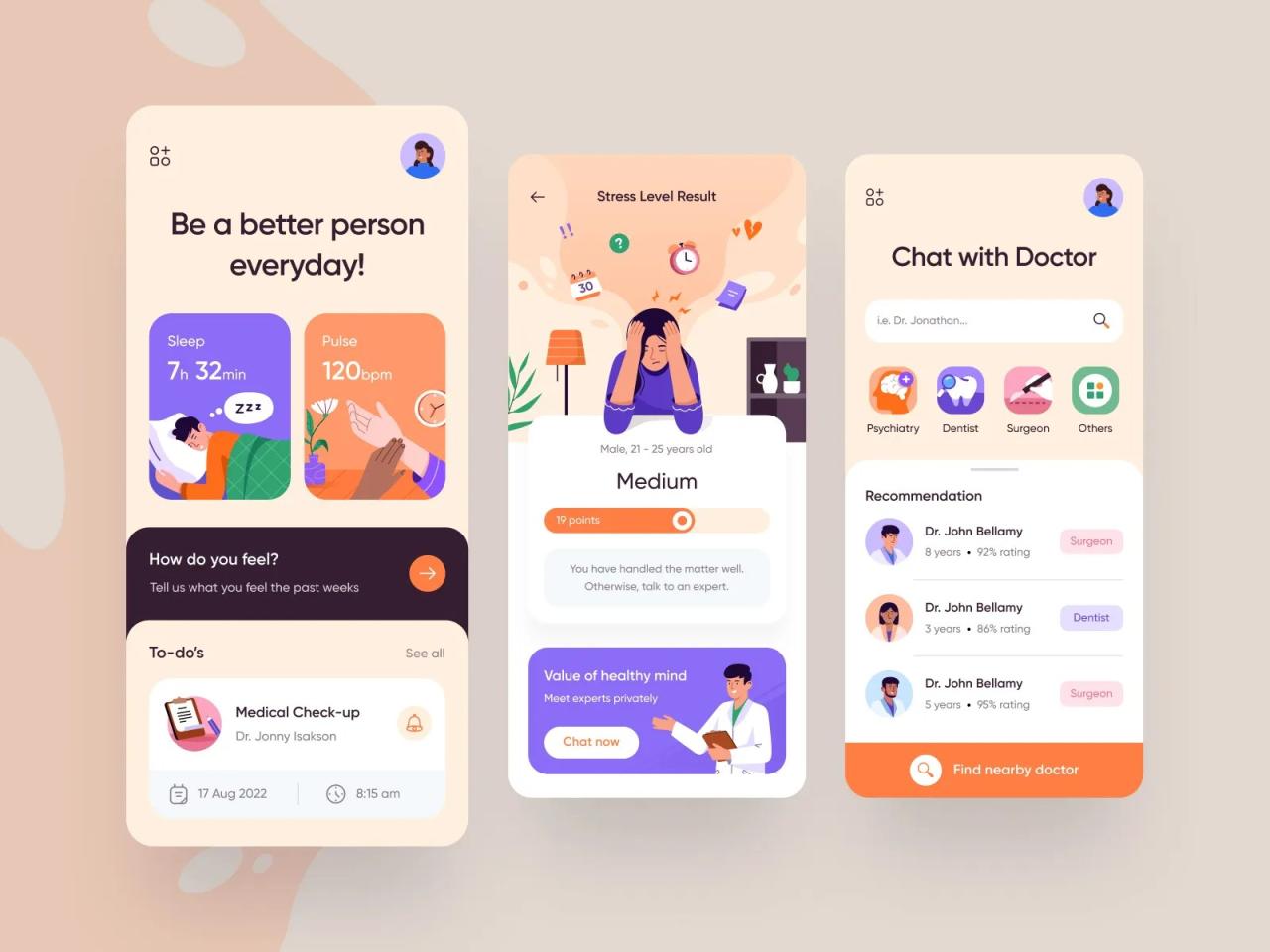
A user-friendly interface is paramount for mobile healthcare applications. A seamless and intuitive design ensures patients can readily access and utilize the app’s features, improving engagement and adherence to treatment plans. This, in turn, positively impacts health outcomes. A well-designed interface fosters trust and confidence, encouraging continued use of the application.A robust user experience (UX) strategy is crucial to the success of a mobile healthcare app.
This entails careful consideration of diverse user needs and preferences, from different age groups to those with varying technological proficiency. It is imperative to design applications that are not only aesthetically pleasing but also highly functional and accessible.
Importance of User-Friendly Interfaces
Effective mobile healthcare apps prioritize user-friendly interfaces to enhance the patient experience. A well-designed interface reduces the cognitive load on users, enabling them to easily navigate the app and access vital information. This, in turn, encourages consistent use and adherence to prescribed health regimens. Intuitive interfaces lead to greater patient satisfaction and a positive perception of the app.
Best Practices for Intuitive Interfaces
Designing intuitive interfaces for diverse user groups requires careful consideration of various factors. Adaptability is key, accommodating different levels of technological proficiency and healthcare literacy. Utilizing clear visual cues and consistent design elements across the application fosters a sense of familiarity and reduces confusion. The language used within the application should be clear, concise, and easily understandable, avoiding jargon or technical terms.
Creating an Effective Navigation System
An effective navigation system within a mobile healthcare app is essential for seamless user experience. Navigation should be intuitive and logical, allowing users to quickly find the information they need. Implementing a hierarchical structure, with clear labels and visual cues, aids users in locating specific features or data. A well-organized navigation system promotes ease of use and user satisfaction.
Improving Accessibility and Usability, Healthcare mobile apps
Accessibility and usability are paramount for inclusive mobile healthcare applications. Features like large font sizes, adjustable text colors, and alternative text for images are essential for users with visual impairments. Providing multiple language options caters to diverse cultural backgrounds. Support for assistive technologies like screen readers ensures that users with disabilities can fully utilize the app. Considering accessibility from the outset of the design process leads to a more inclusive and user-friendly application.
Accessibility Considerations for Different Demographics
| Demographic | Key Aspects of Interface Design |
|---|---|
| Senior Citizens | Large font sizes, clear and concise language, simple navigation, prominent buttons, high contrast colors, avoidance of complex layouts. |
| People with Visual Impairments | High contrast color schemes, large font sizes, alternative text for images, screen reader compatibility, adjustable text sizes. |
| People with Motor Impairments | Large clickable areas, voice input functionality, simplified input fields, use of gestures, alternative input methods. |
| People with Limited Digital Literacy | Simple and straightforward design, clear instructions, minimal technical terms, step-by-step guides, tutorial videos, clear visual representations. |
| People from Diverse Cultural Backgrounds | Multilingual support, cultural sensitivity in design elements, culturally appropriate imagery and language, and adherence to local regulations. |
Data Security and Privacy
Protecting patient data is paramount in mobile healthcare applications. Robust security measures are crucial to maintain user trust and ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of sensitive medical information. Compromised data can lead to significant legal and reputational consequences for the app developers and the healthcare institutions involved.
Significance of Data Security
Data security in mobile healthcare applications is vital for several reasons. First, it safeguards patient privacy, preventing unauthorized access to sensitive medical records. Second, it ensures the integrity of data, preventing tampering or modification. Third, it maintains the availability of data, enabling authorized users to access information when needed. Compromised data can lead to identity theft, financial fraud, and emotional distress for patients.
Patient Data Privacy and Confidentiality Measures
Implementing strong security protocols is essential to protect patient data. These measures should include multi-factor authentication, data encryption both in transit and at rest, and access controls based on roles and permissions. Regular security audits and vulnerability assessments are critical for identifying and mitigating potential threats. Regular updates to the application’s software and operating system are also essential to patch security vulnerabilities.
Compliance Requirements for Sensitive Medical Information
Healthcare data is subject to strict regulations, such as HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) in the US and GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) in Europe. These regulations mandate specific security controls and procedures for handling patient data. Mobile apps must comply with these regulations to avoid legal penalties. These regulations ensure the protection of sensitive personal health information.
Importance of Encryption and Secure Storage Methods
Encryption plays a critical role in protecting patient data. End-to-end encryption ensures that only authorized users can access the data, preventing unauthorized interception. Secure storage methods, such as using trusted cloud platforms with advanced security features, are also crucial. Data should be stored in a secure environment, with access limited to authorized personnel. Data encryption and secure storage are essential for preventing unauthorized access to and modification of patient data.
Data Security Protocols and Effectiveness
| Data Security Protocol | Description | Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|
| End-to-End Encryption | Data is encrypted on the device and decrypted only on the intended recipient’s device, preventing unauthorized access during transmission. | High. Provides strong protection against eavesdropping. |
| Multi-Factor Authentication | Requires multiple authentication methods, such as passwords, security tokens, or biometrics, to verify user identity. | High. Significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access. |
| Regular Security Audits | Systematic evaluations of the security controls and procedures to identify vulnerabilities and potential threats. | Medium to High. Proactive approach to security enhancement. |
| Data Loss Prevention (DLP) | Software solutions to prevent sensitive data from leaving the organization’s control or network. | High. Reduces the risk of data breaches and unauthorized disclosures. |
Technological Advancements and Integration

Mobile healthcare applications are rapidly evolving, driven by a surge in innovative technologies. These advancements promise to revolutionize patient care, empowering individuals with greater access to information and resources. This section explores the transformative potential of emerging technologies in shaping the future of mobile healthcare.The integration of advanced technologies like artificial intelligence, wearable devices, and blockchain is reshaping the landscape of patient engagement, diagnostics, and treatment.
These innovations are not only improving the efficiency of healthcare delivery but also enhancing the overall patient experience.
Role of Emerging Technologies
Emerging technologies are fundamentally altering how healthcare is delivered and experienced. Artificial intelligence, machine learning, wearable sensors, and blockchain are transforming the possibilities within mobile healthcare applications. These technologies are enabling personalized care, predictive analytics, and secure data management, ultimately leading to more efficient and effective healthcare solutions.
Potential of AI and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are poised to significantly enhance mobile healthcare apps. AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of patient data to identify patterns and predict potential health risks. For example, AI-powered apps can monitor vital signs and lifestyle factors to alert users to potential health issues early on. ML models can also be trained to diagnose certain conditions from images, like X-rays or skin lesions, potentially aiding in quicker and more accurate diagnoses.
The ability to personalize treatment plans based on individual patient characteristics is another key advantage of AI and ML.
Integration of Wearable Devices and Sensors
Wearable devices and sensors are increasingly integrated into mobile healthcare applications. These devices continuously monitor various physiological parameters, such as heart rate, sleep patterns, and activity levels. This continuous monitoring allows healthcare providers to track patient progress, identify trends, and intervene early if necessary. For example, apps can track physical activity, sleep quality, and even heart rate variability, providing valuable insights into a user’s overall health.
This data can then be shared with healthcare professionals for a comprehensive health assessment.
Potential of Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology offers a secure and transparent way to manage patient data within mobile healthcare applications. Its decentralized nature ensures data integrity and confidentiality, preventing unauthorized access and tampering. This security is crucial for protecting sensitive patient information. For instance, blockchain can be used to create secure and immutable records of medical history, prescriptions, and consent forms.
This secure, auditable record-keeping is critical for improving patient care coordination and streamlining administrative processes.
Comparison of Technological Advancements
| Technology | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Artificial Intelligence (AI) | AI algorithms analyze data to identify patterns and predict health risks. | Personalized care, early disease detection, improved diagnostics. | Data privacy concerns, potential bias in algorithms. |
| Machine Learning (ML) | ML models learn from data to improve accuracy and efficiency in various tasks. | Accurate diagnoses, personalized treatment plans, improved efficiency. | Requires large datasets for training, potential for overfitting. |
| Wearable Sensors | Continuous monitoring of physiological parameters. | Real-time data collection, early intervention, improved patient engagement. | Data security and privacy concerns, potential for user discomfort. |
| Blockchain | Secure and transparent data management through decentralized ledger. | Data integrity, confidentiality, improved trust and transparency. | Scalability challenges, potential complexity in implementation. |
Mobile Health App Development Trends
Mobile health (mHealth) applications are rapidly evolving, driven by increasing patient demand, technological advancements, and a growing need for accessible and personalized healthcare. This dynamic environment presents both opportunities and challenges for developers, requiring a keen understanding of current trends and future directions.The proliferation of smartphones and readily available internet connectivity has significantly impacted healthcare delivery, enabling the development and widespread adoption of mHealth solutions.
This has led to a significant increase in the volume and variety of mobile health apps, catering to a range of needs, from remote monitoring to mental health support.
Current Trends in mHealth App Development
Current mHealth app development trends emphasize user-centric design, integration with existing healthcare systems, and enhanced data security. Developers are increasingly prioritizing user experience (UX) and intuitive interfaces to ensure seamless engagement and adoption. Furthermore, the integration of mHealth apps with Electronic Health Records (EHRs) is becoming a critical aspect of streamlining patient care. The emphasis on secure data handling and robust privacy protocols reflects the increasing importance of patient trust and regulatory compliance.
Growth of mHealth Solutions by Region
The adoption of mHealth solutions varies significantly across regions, influenced by factors like healthcare infrastructure, economic development, and cultural norms. Developing nations often face challenges in implementing mHealth due to limited access to technology and reliable internet connectivity. However, the growth of mHealth is demonstrably rapid in regions with robust telecommunication networks and a growing middle class, as witnessed by the increasing use of telehealth platforms for virtual consultations.
The Asia-Pacific region, for instance, is experiencing substantial growth in mHealth adoption, fueled by a young population and expanding digital infrastructure.
Healthcare mobile apps are becoming increasingly prevalent, offering convenient access to medical information and services. These apps are just one facet of the broader world of mobile applications, encompassing a vast range of functionalities. Exploring the broader category of mobile applications reveals the potential for further innovation in healthcare, ultimately improving patient care through streamlined processes and readily available tools.
Challenges Faced by mHealth App Developers
Developing and deploying successful mHealth applications presents several significant challenges. One key concern is maintaining data security and privacy, as mHealth apps often handle sensitive patient information. Ensuring regulatory compliance with HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) or similar regulations is crucial for avoiding legal issues. Another challenge involves integrating mHealth applications with existing healthcare systems, a process that often requires significant technical expertise and resources.
Furthermore, maintaining user engagement and ensuring ongoing app usage can be a significant obstacle, requiring continuous improvement and adaptation to evolving user needs.
Future Direction of mHealth Innovation
The future of mHealth innovation will likely focus on personalization and AI-powered solutions. This includes the development of AI-driven diagnostic tools, personalized treatment plans, and predictive models for identifying at-risk patients. The integration of wearable devices for continuous health monitoring will play an increasingly important role, providing real-time data for personalized interventions and proactive healthcare management. Remote patient monitoring (RPM) will continue to be a major area of development, potentially revolutionizing the delivery of care in remote or underserved communities.
Steps in Designing a Prototype for a Mobile Healthcare Application
A well-structured prototype is critical for the success of any mHealth application. The design process typically begins with defining the target user group and understanding their needs and pain points. This often involves conducting user interviews and surveys to gain valuable insights. Following this, a detailed understanding of the application’s functionalities and features is essential. Wireframing and mockups are created to visualize the app’s user interface, ensuring intuitive navigation and a positive user experience.
This iterative design process allows for feedback and refinement based on user testing, ultimately leading to a robust and user-friendly final product.
Market Analysis and Competition
The mobile healthcare app market is experiencing rapid growth, driven by increasing smartphone adoption, rising healthcare costs, and the need for convenient and accessible healthcare services. This sector presents substantial potential for innovation and profitability, but also intense competition. Understanding the market dynamics and competitive landscape is crucial for developing successful mobile healthcare applications.
Market Size and Growth Potential
The mobile healthcare app market is substantial and continues to expand. Studies indicate a significant increase in the number of users utilizing these applications for various healthcare needs, from scheduling appointments to managing chronic conditions. The projected growth hinges on factors like technological advancements, rising healthcare costs, and growing demand for accessible care. For example, the telehealth market is experiencing a surge, demonstrating the growing appeal of virtual consultations and remote monitoring.
This expansion is likely to be fueled by the ongoing trend of preventive care and proactive health management.
Key Players and Competitors
Several established players and emerging startups are vying for market share in the mobile healthcare space. Large tech companies, established healthcare providers, and specialized health technology companies all compete for a piece of this expanding market. Examples include companies like Teladoc, MDLive, and numerous hospital systems offering their own patient portals and apps. This competitive landscape necessitates a clear understanding of the unique value proposition and target market for any new mobile healthcare application.
Competitive Landscape and Strategies for Success
Success in the mobile healthcare app market hinges on differentiation. Applications need to offer distinct value propositions beyond existing offerings. This could include innovative features, superior user experience, strategic partnerships with healthcare providers, or targeted niche markets. Competitive strategies should also focus on building a strong brand, leveraging marketing effectively, and establishing strong relationships with healthcare providers and insurance companies.
This approach can effectively position the application to stand out in a crowded marketplace.
Business Models for Mobile Healthcare Applications
Various business models are employed in the mobile healthcare app industry. These include freemium models, subscription models, and pay-per-use models. The freemium model, offering basic features for free with premium features accessible through subscriptions, is quite common. Some applications also partner with insurance companies to offer their services as part of a comprehensive health plan. The choice of business model should align with the application’s features, target audience, and revenue goals.
Comparison of Leading Mobile Healthcare Apps
| App Name | Key Features | Target Audience | Business Model |
|---|---|---|---|
| Teladoc | Virtual consultations, remote monitoring, chronic condition management | Wide range of patients seeking convenient access to care | Subscription and pay-per-use |
| MDLive | Virtual primary care, specialist consultations, prescription refills | Patients seeking urgent care and convenient access to healthcare professionals | Subscription and pay-per-use |
| [Example App 3] | Medication reminders, health tracking, appointment scheduling | Patients focused on proactive health management and convenience | Freemium |
The table above provides a simplified comparison of leading mobile healthcare apps. Actual features and models may vary, and new apps frequently emerge, altering the competitive landscape. This table highlights the range of approaches taken by various players.
Mobile Health Applications for Specific Populations
Mobile health (mHealth) apps are increasingly recognized as valuable tools for improving health outcomes and promoting well-being across diverse populations. Tailoring these applications to specific needs, cultural contexts, and health conditions enhances accessibility and effectiveness. This approach ensures that individuals from various backgrounds can benefit from the advantages of digital health interventions.These applications go beyond generic health monitoring and provide personalized support for specific health conditions, offering tailored interventions and empowering users to take proactive steps toward improved health.
This personalized approach is crucial for promoting health equity and addressing disparities in healthcare access.
Specific Populations Benefiting from mHealth Apps
Various demographics stand to gain from dedicated mHealth applications. The elderly, often facing challenges with mobility and social isolation, can leverage apps for medication reminders, appointment scheduling, and social connection. Similarly, individuals with chronic illnesses, such as diabetes or heart conditions, can benefit from apps providing personalized monitoring, education, and support for managing their conditions. Mental health apps are proving vital for individuals struggling with stress, anxiety, or depression, offering tools for self-management and connecting them with resources.
Features Tailored to Specific Demographics
The design of mHealth applications should consider the specific needs and preferences of each target demographic. For example, applications designed for the elderly should prioritize large font sizes, intuitive navigation, and clear instructions. Accessibility features, such as voice commands and text-to-speech functionality, are critical for ensuring usability. Apps for chronically ill individuals should include comprehensive health data tracking, personalized recommendations, and access to medical professionals.
Healthcare mobile apps are becoming increasingly prevalent, offering convenient access to various medical services. Developing these apps requires a strong foundation in mobile app development , ensuring user-friendliness and robust functionality. Ultimately, these apps are a crucial component of modern healthcare delivery.
Apps for mental health should offer tools for stress management, mindfulness exercises, and secure communication channels for support.
Role of mHealth Apps in Promoting Health Equity
Mobile health apps can play a vital role in promoting health equity by providing accessible and affordable healthcare resources. These tools can bridge the gap in access to healthcare for underserved populations, especially those living in rural areas or with limited access to traditional medical services. By providing culturally appropriate information and support, mHealth apps can help address health disparities and improve overall health outcomes.
Apps can provide language support and culturally sensitive content, enhancing inclusivity.
Cultural Considerations in mHealth App Design
Designing mHealth applications for diverse populations necessitates careful consideration of cultural norms and sensitivities. Language support is crucial, as is the representation of diverse perspectives and experiences in the app’s design and content. Cultural nuances in communication styles, beliefs, and healthcare practices should be taken into account to ensure the app is both effective and respectful. This includes considering potential variations in the understanding and acceptance of technology usage.
Tailoring Apps for Specific Conditions
Mobile health apps can be tailored to specific health conditions, providing personalized interventions and support. For diabetes management, apps can track blood glucose levels, provide meal planning suggestions, and offer reminders for medication and exercise. Mental health apps can offer tools for stress reduction, mindfulness practices, and access to mental health professionals. By providing condition-specific information and support, mHealth apps can empower users to actively manage their health.
Examples include apps for managing asthma, hypertension, and chronic pain.
Impact on Healthcare Delivery and Outcomes
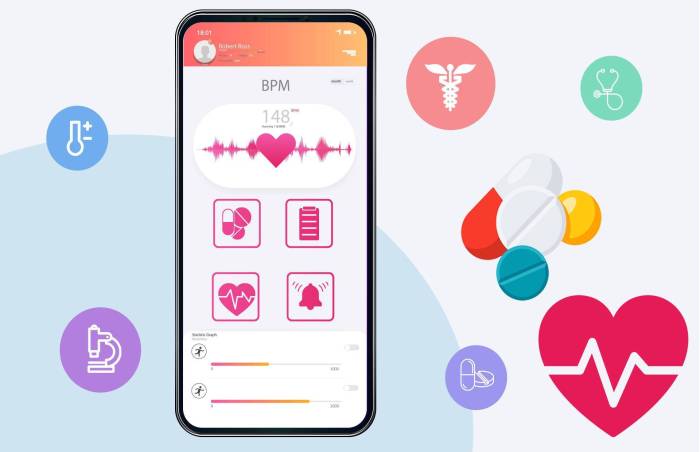
Mobile healthcare applications are revolutionizing the delivery of healthcare services, offering a range of benefits for patients and providers alike. These apps streamline processes, enhance patient engagement, and ultimately contribute to improved health outcomes. By providing convenient access to information and resources, mobile apps are shaping the future of healthcare.Mobile health applications have demonstrably altered healthcare delivery models.
Their ability to facilitate remote monitoring, virtual consultations, and personalized treatment plans has profoundly influenced the efficiency and accessibility of care. These technologies empower patients to take greater control of their health journey, while simultaneously supporting healthcare professionals in delivering more comprehensive and timely interventions.
Impact on Efficiency of Healthcare Delivery
Mobile apps have the potential to significantly enhance the efficiency of healthcare delivery by automating administrative tasks, facilitating seamless communication, and enabling remote monitoring. Streamlined appointment scheduling, electronic health record integration, and remote patient monitoring reduce wait times and improve overall operational efficiency. For example, telehealth platforms allow providers to conduct virtual consultations with patients in remote areas, reducing travel time and costs for both patients and providers.
Influence on Patient Engagement and Adherence
Mobile health apps can positively impact patient engagement and adherence to treatment plans by providing personalized support and reminders. Interactive tools, educational materials, and progress tracking features encourage patients to actively participate in their care. For instance, apps can send personalized medication reminders, offer interactive exercises, and provide educational content related to specific conditions, fostering greater patient engagement and adherence to treatment protocols.
Effectiveness in Improving Health Outcomes
Mobile healthcare apps can contribute to improved health outcomes by enabling proactive health management, personalized interventions, and timely access to care. Remote patient monitoring systems can detect subtle changes in vital signs, enabling early interventions and preventing potentially serious complications. Personalized treatment plans, tailored to individual patient needs, can improve adherence and optimize outcomes.
Impact on Healthcare Costs
The impact of mobile health apps on healthcare costs is multifaceted. While some apps may involve initial investment costs, potential cost savings can arise from reduced hospital readmissions, improved patient adherence, and reduced need for in-person visits. By promoting preventative care and early intervention, mobile health applications can contribute to long-term cost savings.
Comparison of Traditional vs. Mobile Healthcare Solutions
| Feature | Traditional Healthcare | Mobile Healthcare |
|---|---|---|
| Cost of Initial Investment | High, often requiring significant capital expenditure for infrastructure and equipment. | Moderate, requiring investment in software and potentially hardware, but often lower than traditional methods. |
| Accessibility | Limited by geographic location and scheduling constraints. | Broader accessibility, allowing patients to access care anytime, anywhere. |
| Efficiency | Often involves lengthy wait times for appointments and processing of information. | Potentially higher efficiency through streamlined communication and automation of tasks. |
| Patient Engagement | Patient engagement often limited to passively receiving information. | Promotes active patient participation through personalized support, reminders, and interactive tools. |
| Cost Savings | Potential for high costs associated with hospital readmissions and unnecessary procedures. | Potential for cost savings through early interventions, reduced hospitalizations, and improved patient adherence. |
Mobile health applications, when effectively implemented, can contribute to a more efficient, accessible, and cost-effective healthcare system.
Ethical Considerations and Challenges: Healthcare Mobile Apps
Mobile healthcare applications offer significant potential to improve access and quality of care, but their implementation necessitates careful consideration of ethical implications. The digital nature of these platforms introduces unique challenges regarding data privacy, potential biases, and the need for transparency and accountability. These concerns must be addressed proactively to ensure equitable and responsible use of mobile health technologies.The use of mobile health applications raises several ethical concerns that must be carefully navigated.
These applications often collect sensitive patient data, which necessitates robust safeguards to protect patient privacy and confidentiality. Furthermore, the potential for bias in algorithms and the limited access to technology in certain populations can exacerbate existing health disparities. Developing and deploying these applications responsibly requires a commitment to ethical principles and a proactive approach to addressing potential issues.
Privacy Concerns Related to Data Collection and Usage
Protecting patient data is paramount. Mobile health apps often collect and store vast amounts of personal health information. Data breaches or unauthorized access can have severe consequences, jeopardizing patient trust and potentially leading to harm. Strict adherence to data protection regulations, such as HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) in the US, is crucial. Implementing strong encryption, access controls, and secure data storage methods are vital for safeguarding patient information.
Transparent data usage policies, outlining how data will be collected, stored, and used, are essential for building patient trust.
Potential Biases and Limitations of Mobile Health Technologies
Mobile health technologies can inadvertently perpetuate existing health disparities. Algorithms used in these applications may reflect biases present in the data they are trained on, potentially leading to inaccurate diagnoses or unequal access to care. Limited access to technology or digital literacy among certain populations can create barriers to participation, further marginalizing those who need care the most.
Developers must actively strive to identify and mitigate potential biases in their applications and ensure equitable access for all. Addressing the digital divide is critical to ensure inclusivity and fairness in the use of mobile health technologies.
Importance of Transparency and Accountability in Mobile Healthcare Apps
Transparency in the development, implementation, and operation of mobile healthcare applications is essential. Clear communication about data collection practices, algorithm use, and potential limitations is crucial for building patient trust. Accountability mechanisms are needed to ensure that developers and providers are held responsible for the ethical and effective use of these technologies. Independent audits and evaluations of the applications’ performance and impact are critical for maintaining ethical standards and public trust.
Ethical Guidelines for the Development and Implementation of Mobile Healthcare Apps
To ensure the responsible development and deployment of mobile healthcare applications, the following guidelines are essential:
- Data Minimization: Collect only the necessary data, using anonymization techniques whenever possible, to minimize the amount of sensitive information stored and accessed. This protects patient privacy and reduces the risk of breaches.
- Data Security: Implement robust security measures to protect patient data from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, alteration, or destruction. This includes using strong encryption, access controls, and secure storage methods.
- Bias Mitigation: Actively identify and mitigate biases in algorithms and data sets used in mobile health applications. This involves employing diverse data sets and rigorous testing protocols.
- Accessibility and Inclusivity: Design mobile health applications to be accessible to all populations, including those with limited access to technology or digital literacy. Accessibility should be a core consideration throughout the development process.
- Transparency and User Control: Provide clear and concise information about data collection, usage, and privacy policies. Give users control over their data, including the ability to access, correct, and delete their information.
- Continuous Monitoring and Evaluation: Implement mechanisms for continuous monitoring and evaluation of the application’s performance and impact. This includes gathering feedback from users and evaluating the application’s effectiveness in addressing health disparities.
Epilogue
In conclusion, healthcare mobile apps are rapidly transforming healthcare delivery, empowering patients, and improving health outcomes. However, the ethical implications, security protocols, and user experience design must be meticulously considered to ensure the responsible and effective use of these powerful tools. This guide provides a thorough overview, highlighting the key considerations for developers, users, and healthcare providers.
Quick FAQs
What are the key security concerns regarding healthcare mobile apps?
Protecting patient data is paramount. Robust encryption, secure storage methods, and adherence to privacy regulations like HIPAA are crucial. Regular security audits and vulnerability assessments are essential.
How do healthcare mobile apps improve patient engagement?
Apps facilitate convenient access to information, reminders for appointments and medication, and opportunities for interaction with healthcare providers. This fosters better adherence to treatment plans and promotes proactive health management.
What are the common challenges faced by developers of healthcare mobile apps?
Balancing user experience with robust security features, addressing diverse user needs, and ensuring regulatory compliance present ongoing challenges. Cost-effective development and maintenance are also significant factors.
How can mobile health apps address the needs of specific populations?
By incorporating culturally sensitive design, language options, and features tailored to specific conditions or needs, healthcare mobile apps can be effective for various populations. Examples include diabetes management apps or apps supporting mental health needs.





